
How Far is Too Far? A Discussion on Maximum Seating Distance
Rarely does the design of a performing arts facility progress very far before the architect looks up from the tracing paper and asks the theatre consultant the inevitable question, "What is the maximum distance from the stage to the last row?" Any architect who has done more than one theatre - and therefore has asked that question more than once - knows that there is no answer to that question; or rather that there are many answers. In fact, there are probably more answers that there are theatre consultants.
Every theatre consultant has her or his own way of answering this question. In some cases the consultant will venture forth with an actual dimension - and then usually proceed to qualify that dimension in a number of different ways. Others will take this opportunity to expound on issues such as intimacy, clarity, sight lines, acoustics, and the dramatic experience - all of which will eventually come round to a conclusion that the distance from the stage to the last row is less important than the design of everything between the stage and the last row.
There are published studies, experiments, and precedents - but not many. The noted American scene designer Jo Mielziener, in his book The Shapes of Our Theatres, related an experiment that he conducted in 1960, in preparation for consulting on the Vivian Beaumonet Theatre at Lincoln Center.
I decided to make field tests to determine the maximum acceptable distance between performers and the most distant row of the audience. How far can the last rows of seats be and still retain a sense of visual contact with the stage...to appreciate the subtle expressions of an actor's face and eyes? I divided my tests into two general categories: drama and legitimate comedy, and musical theatre. Within each category, I picked out artists whose visual characteristics would cover a wide range. I studied Julie Harris...[and] found it impossible to appreciate her features from the back of a large house. then, moving to seats that were 50-55 feet from the stage, I found that I could fully enjoy her most subtle facial expressions. I witnesses many other performances, some in the broader style of musical comedy. The broad expressions and gestures, not to mention tremendous vocal projection of an Ethel Merman, can carry to rows over 100 feet away without too costly a lot of visual enjoyment. here a completely different scale had to be used, primarily because of the music and movement - dance, breadth of gesture, and style of acting. The conclusion was obvious: each type of presentation style had its acceptable limits in scale. In terms of actual distance, in the legitimate field it is some 60to 70 feet before a discernible, but decisive fall-off of visual appreciation appears. In the musical field, these distances can be extended half again as much.
The October 1984 issue of the Japanese publication, Theatre Technology, contains the article, "An Experiment in Visual Acuity Affecting Audience Seating." This article documented a series of experiments conducted between 1964 and 1977 by Dr. Shizuo Toyama to determine the greatest acceptable distance between the spectator and stage. These experiments used Landolts Rings of appropriate dimensions to represent the main component of a performer's facial expression, the movement of the eyes. De. Toyama's team measured the longest distance at which the orientations of these Landolts Rings could be distinguished, using test audiences. These experiments did not distinguish between performance styles, but did differentiate between the brightness of the lighting on stage. At 500 lux (50 foot-candles), the average maximum distance was 31.6 meters (104 feet), and at 1,000 lux (100 foot-candles), the average maximum distance was 34.5 meters (113 feet).
In his book Theatre Design, George C. Izenour explains his general criteria of 80 feet for drama and 120 feet for Opera.
Ideally legitimate theater requires each member of the audience to be able to see the actor's changing facial expressions, which can vary widely, depending upon lighting conditions, makeup, and distance from the stage. Opera, being more presentational than theater, requires the singer-actor to act in a more deliberate and stylized manner than the legitimate theater act. Opera makeup is also more exaggerated and the music helps convey the emotive quality of the scene. The seeing distances for seated spectators used here are considered as average maximums. Some authorities advocate 10 percent less than those used here; still others allow 10 to 15 percent more.
As part of his preparation for the design of the National Theatre in London over two decades ago, Richard Pilbrow of Theatre Projects Consultants conducted a series of test using actors in a number of West End theatres. The group participating in the test included Sir Laurence Olivier and members of the National Company of the time, both performing and judging the results. In the end, Sir Laurence concluded that nobody could adequately watch him perform from more than 65 feet away. This dimension drove the designs of both Olivier and Lytteleton theatres. In the Olivier, with a modified thrust and 120-degree audience fan, it was possible to place 1,600 seats on two levels and still keep the last row within 65 feet. In the Lyttleton, the proscenium configuration allowed only 960 seats to be placed on two levels in front of a 48-foot-wide stage, once again keeping the last row to within 65 feet.
There are a number of variables that must be considered in this context. If a production is dimly lighted (or poorly lighted), a viewer in the third row may feel distanced. Performers that are not fully trained, such as in an academic theatre production, will have difficulty connecting with the audience members much less than 65 feet from the stage. In addition, audiences have different levels of expectation depending on the venue and depending on their age. Audience members who have paid $40 for a professional resident theatre production may expect to see and hear better than audiences for school performances. And younger audiences, weaned on 45-inch video screens with surround-sound audio, may have higher expectations for seeing and hearing than their older counterparts.
most theatre consultants agree that acceptable maximum viewing distances vary with the type of performance. Those theatre consultants that are willing to apply numbers to this exercise do so only by categorizing those numbers by performance type. Michael Mell uses a rule of thumb of 60 feet on the main floor/80 feet in the balcony for drama theatres, and he adds 10 to 20 feet for theatres that present musicals and opera. mell says, "I want to see the whites of their eyes!"
Jim Read points out the importance of distinguishing the actor's features and doesn't like working beyond 75 feet for theatre and 100 feet for musicals and opera. Edgar L. Lustig uses a sliding scale that accepts 60 feet for small academic theatres, 80 feet for theatres seating up to 1,400, and 115 feet for theatres as large as 3,000. Jack Hagler tries to limit the last row to within 80 feet "for theatres where facial expressions are important." Hagler, who has consulted on several theme park theatres, finds that acceptable maximum distances in those venues are typically higher - often in excess of 125 feet.
Acoustics are obviously a factor. R. Duane Wilson, who generally relies on he Izenour criteria of 80 feet for dram and 120 feet for musicals and opera, applies these criteria from an acoustical standpoint. Wilson says, "For me the real criteria is not distance per se, but the resulting volume and its effect on reverberation. A 2,500-seat modern church will be acceptable at 152 feet only because all events will be amplified and the room will be totally absorptive. basically there will be no reverberant field. [The maximum] is that distance where the reverberant field becomes unacceptable."
Where hearing is of primary importance to one theatre consultant, other olfactory senses are important to others. Armand Marion's credo is, "If you can't smell the actors, then you are too far away!" (When this rule of thumb fails, Marion uses 60 feet).
Robert Long, who generally uses 65 feet for drama and 120 feet for opera and musicals, quickly goes on to explain, "Each live performing art tends to dictate the scale upon which it can be successfully performed. Eventually satisfaction for each audience will depend both upon the radiated power of the human performer and the degree of arousal and response engendered as individual spectators are transformed into a collective audience. Issues of sufficient three-dimensional "crowding," increased sense of mutual awareness and psychological reaction dictated by the environment surrounding the performance, all play a part in creating great live performance space."
Robert Davis refuses to identify specific maximum distances. he says, "The acceptable distance depends heavily on the production style and experience level of the actors and director. There are no golden numbers. How do we make the audience feel connected to the performance? In designing a room, every action we take is made with audience focus in mind. Every line, every surface, every material, and every ray of light in the auditorium should be helping the whole audience connect to the performance."
New Aronoff Center Opens in Cincinnati
 Downtown Cincinnati got a major boost in October, 1995, when the Aronoff Center for the Arts opened. The grand new center (project cost: $82 million) includes three lively performance spaces, the Alice F. and Harris K. Weston Art Gallery, and the Plaza 600 restaurant. Architect for the complex was Cesar Pelli & Associates, New Haven, Connecticut; the associate architect, was Gartner Burdick Bauer-Nilson, Columbus, Ohio. The theatre consultant was Theatre Projects Consultants, Ridgefield, Connecticut; and R.L. Kirkegaard & Associates, Downers Grove, Illinois, was the acoustics consultant. The architectural lighting was designed by Theatre Projects Consultants.
Downtown Cincinnati got a major boost in October, 1995, when the Aronoff Center for the Arts opened. The grand new center (project cost: $82 million) includes three lively performance spaces, the Alice F. and Harris K. Weston Art Gallery, and the Plaza 600 restaurant. Architect for the complex was Cesar Pelli & Associates, New Haven, Connecticut; the associate architect, was Gartner Burdick Bauer-Nilson, Columbus, Ohio. The theatre consultant was Theatre Projects Consultants, Ridgefield, Connecticut; and R.L. Kirkegaard & Associates, Downers Grove, Illinois, was the acoustics consultant. The architectural lighting was designed by Theatre Projects Consultants.
The largest performance space is Proctor & Gamble Hall, a 2,700-seat theatre with an amazingly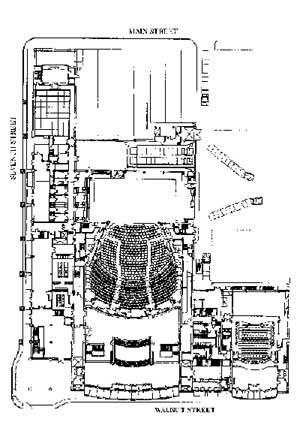 intimate atmosphere. It is fully equipped to support the demands of large-scale Broadway productions, the Cincinnati Ballet, and a wide range of major drama, opera, dance, and headliner productions. The proscenium is 52 feet wide and 38 feet high. The stage is 114 feet wide and 54 feet deep. Over the stage is a system of 94 single-purchase counterweight line sets. The first three rows of auditorium seats are on portable platforms which can be removes to create and expanded orchestra pit for up to 80 musicians. there are two loading doors, allowing up to four semi-trailer trucks to unload simultaneously.
intimate atmosphere. It is fully equipped to support the demands of large-scale Broadway productions, the Cincinnati Ballet, and a wide range of major drama, opera, dance, and headliner productions. The proscenium is 52 feet wide and 38 feet high. The stage is 114 feet wide and 54 feet deep. Over the stage is a system of 94 single-purchase counterweight line sets. The first three rows of auditorium seats are on portable platforms which can be removes to create and expanded orchestra pit for up to 80 musicians. there are two loading doors, allowing up to four semi-trailer trucks to unload simultaneously.
The Jarson-Kaplan Theatre is a 440-seat proscenium theatre with full production capabilities hosting a variety of local and regional performance groups. The house consists of a central seating area surrounded by a raised lodge level and two balconies with seating down the side walls. An orchestra pit, additional seating, or a stage extension can be created by means of a pit elevator. The proscenium is 40 feet wide and the stage is 72 feet wide by 27 feet deep. There are 39 sets of single-purchase counterweights over the stage.
The third performance space is the Fifth Third Bank Theatre. This flexible studio space is a flat-floored room, 44 feet by 52 feet, with a pipe grid positioned at 18 feet above the floor. Modular stage and seating risers provide maximum flexibility, with seating or approximately 150. This entire area has a resilient wood floor suitable for dance.
All three performances spaces have full state-of-the-art lighting and sound and communications systems.
ASTC Holds Winter Business Meeting
The membership of the ASTC gathered on February 10 and 11 a the Park Hyatt Hotel in Chicago for its semi-annual business meeting. The meeting began with a tour of the Civic Opera House, home of Lyric Opera of Chicago. The tour was conducted by Duane Schuler, resident lighting designer for Lyric Opera and a principal theatre consultant with Schuler & Shook, Inc. The Civic Opera House is currently in Phase Three of a four-phase renovation. A major part of this renovation was the conversion of the former Civic Theatre, behind the stage of the Civic Opera House, into a new scenery handling area, dressing rooms, and three large rehearsal rooms. The project also includes complete renovation of the rigging, lighting, and sound systems. ASTC members had the opportunity to walk the highest rigging gridiron in the world, 145 feet above the Civic Opera House stage.
There was considerable discussion of membership, including eligibility requirements and upgrading of membership. The Board of Directors voted to amend the ASTC By-Laws to delete the requirement for U.S. citizenship.
Several members made short presentations on completed projects, methods, materials, and other topics of interest. Among the presentations were the Disney Institute (Ted Boys), Portsmouth, Ohio, Performing Arts Center (Jim Read), Greek Theatre renovations (Robert Davis), Trans World Dome (Edgar Lustig), and Snug Harbor (Michael Mell).
This summer's Forum will be held on July 26, 27, 28 in Quebec City, Quebec. There will be two points of primary focus: (1) general discussion of the future direction for the ASTC, and (2) preparing for a large-scale conference on theatre renovation and adaptive re-use the following year. Next winter's business meeting will be held March 18, 1997 in Pittsburg. This will be in conjunction with the Congress of the OISTAT and the National Convention of USITT.